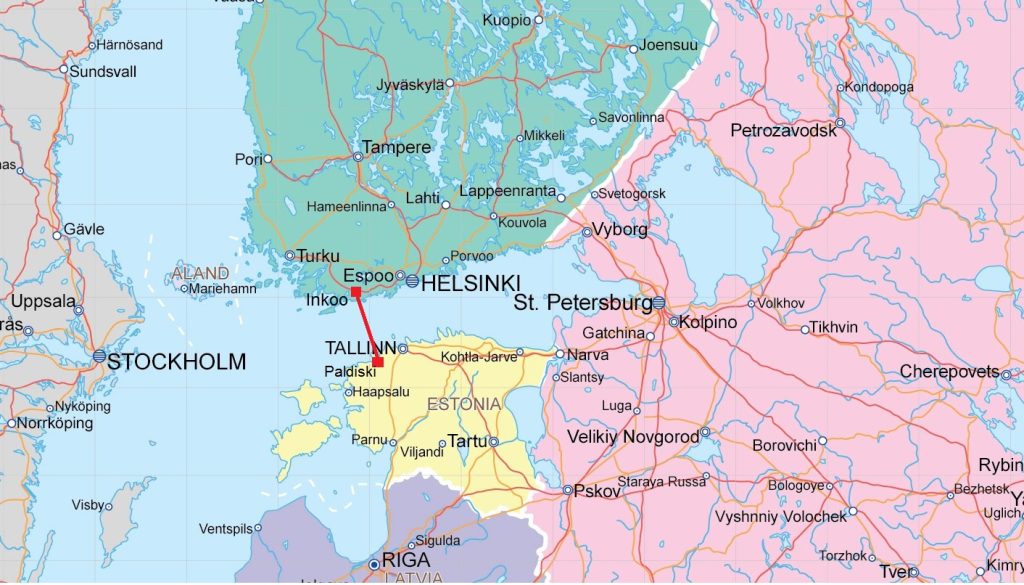
Balticconnector on the map
Balticconnector on the map in life
The Balticconnector is an important natural gas pipeline running underwater between Finland and Estonia. As a geographer who studies pipeline infrastructure, I’m often asked about the exact route and location of the Balticconnector. In this article, I’ll walk you through its path on the map and discuss why its location is strategically important.
What does the Balticconnector gas pipeline provide?
But first, let’s zoom out and understand the context. The Balticconnector is part of a push by the European Union to better integrate the gas markets of its member states. By linking the gas grids of Finland and Estonia, the Balticconnector allows gas to flow in both directions. This gives Finland access to gas sources beyond Russia, and gives Estonia access to the Nordic gas market. Pretty neat right?
Where is Balticconnector?
Now let’s dive into the specifics. The Balticconnector pipeline begins on the Finnish side at an industrial area in Inkoo, about 60km west of Helsinki. It travels 105km across the Gulf of Finland, passing near several small islands along the way. Finally, it makes landfall in northeast Estonia, connecting to the Estonian gas transmission system near the town of Paldiski. The entire underwater route stays within the territorial waters of Finland and Estonia – no need to get other countries involved!
You might be wondering, why was this particular route chosen? Well, it’s the shortest distance between the Finnish and Estonian gas grids. Going further north or south would have meant a longer, more expensive pipeline. It also avoids passing through any major ship traffic lanes in the Gulf of Finland. Short, simple, and cost-effective – that’s how we engineers like it!
The construction of the Balticconnector was no small feat. Building a 105km underwater pipeline required some sophisticated engineering. The water depths along the route range from 60 to 80 meters – too deep for traditional pipeline laying. So they used a special pipe-laying vessel equipped with dynamic positioning to carefully place the pipe on the seabed. Tricky stuff!
What does Balticconnector provide?
Now that it’s operational, the Balticconnector pipeline allows up to 7.2 million cubic meters of natural gas per day to flow between Finland and Estonia. That’s enough to supply over 80,000 Finnish households! By integrating our energy infrastructure, the Balticconnector brings both countries closer together, physically and economically.
I hope this give you a good sense of where the Balticconnector is located and why it’s an important energy link between Finland and Estonia. Let me know if you have any other questions! As a geographer, I always enjoy chatting about infrastructure mapping and development. The Balticconnector is a great example of how modern pipeline engineering can help improve energy security and cooperation.
 The Guide Maps
The Guide Maps