Map of Ethiopia
Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia map online
General description of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia
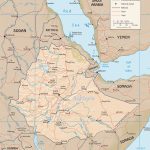
The Republic of Ethiopia on the map can be found in the northern part of East Africa. It is the largest state in the region – 1,104,300 sq. km. The closest territory is Tanzania, which extends over less than 1,000 square kilometers. km. However, in Africa as a whole, Ethiopia is inferior in size to no less than a dozen states. Such as Algeria, Congo, Sudan, South Africa and others.
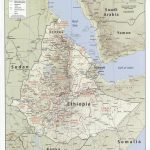
The largest river in the country is located in the west of Abbay, also called the Blue Nile. This name is explained by the fact that this water artery feeds the Nile and for some time it was believed that it was its source that was the source of the great river. The eastern part of Ethiopia is arid, and therefore it is more difficult with rivers, but Jubba stands out among them , already in neighboring Somalia turning into a full-flowing river.
Ethiopia has the highest average altitude among African countries. This highland is called the Ethiopian. However, all of the country’s highest mountains are in the north. Of these, Ras Dashen and Talo are the highest. The first has a height of 4620 m, and the second – 4413.
The climate in most of the country, despite its location in the subequatorial and equatorial climatic zones, does without extreme temperatures. Which is explained by the highlands. However, the eastern, lowland part suffers just from them. The semi-desert rocky landscape and relatively rarefied air make Ethiopia a place where high daily temperature fluctuations are not uncommon. The difference between night and day air temperature can be 15-20 degrees Celsius.
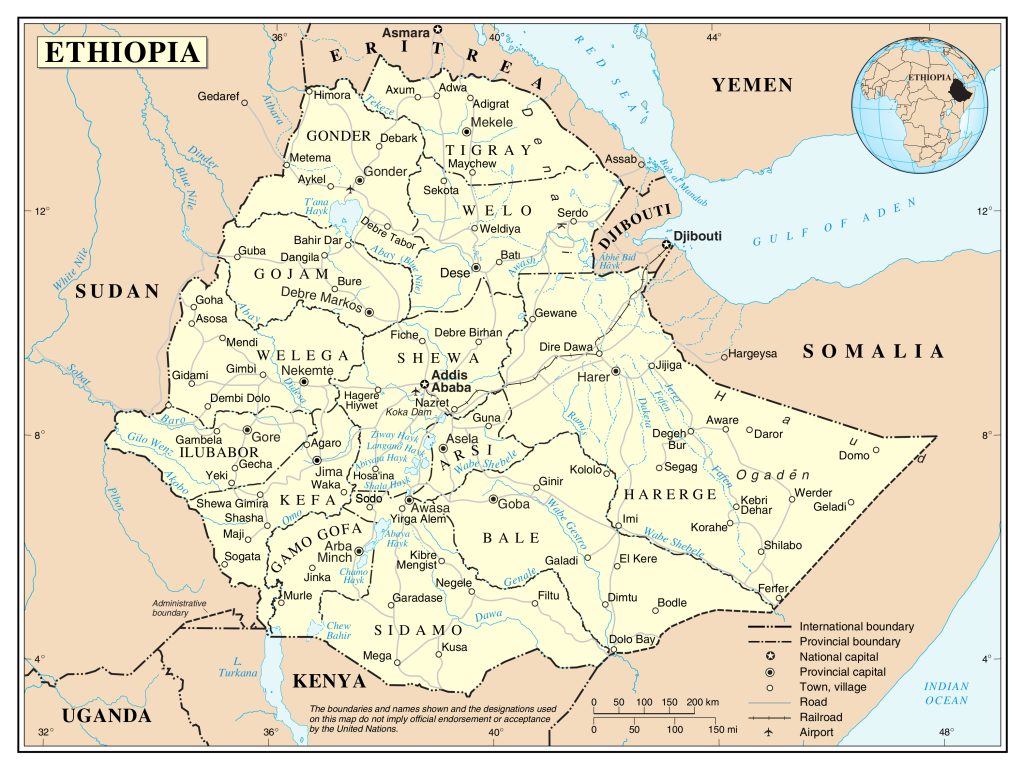
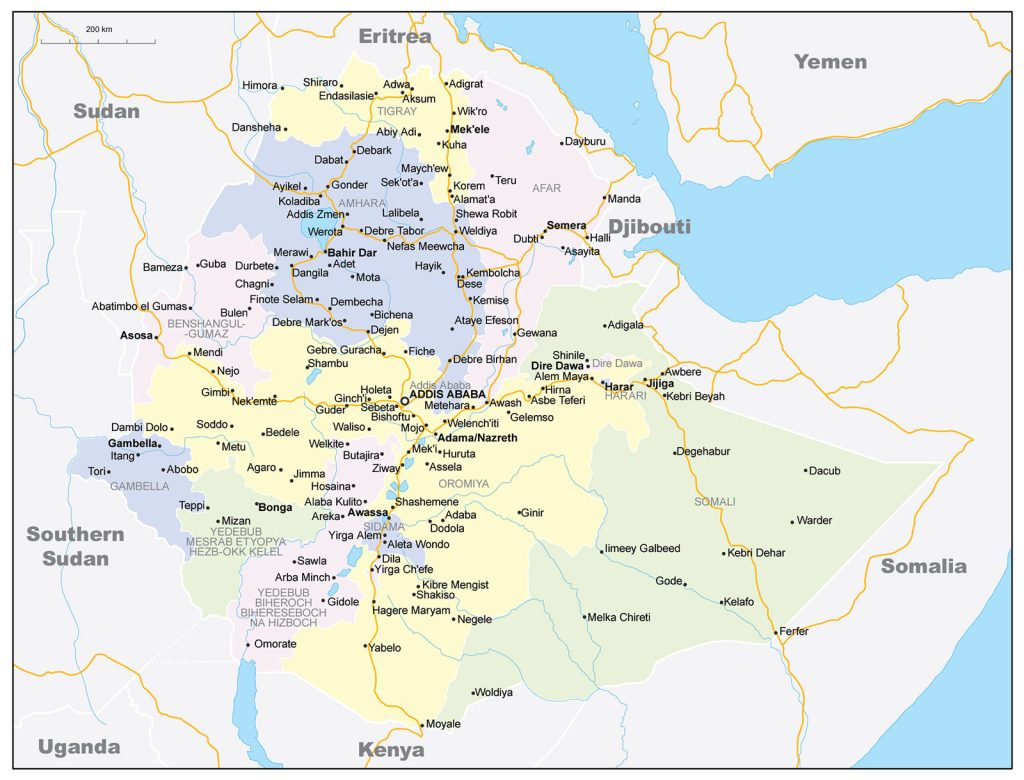
The capital of Ethiopia – Addis Ababa (population of about 4 million inhabitants) – is located almost in the geometric center of the country in the highlands. The nodal position of the city is also emphasized by the transport network.
Other major Ethiopian cities on the map of Ethiopia are:
- Dire-Dawa – a population of about 400 thousand people;
- Nazret – 300;
- Gondar – 260;
- Mekelle – 220;
- Dessie – 220;
- Bahir Dar – 220;
- Jimma – 210;
- Debre Zebit – 180.
Location of Ethiopia on the world map
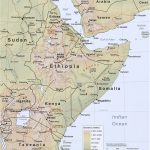
Ethiopia is located in the northern, high-mountainous part of East Africa, west of the so-called Horn of Africa – the eastern tip of Africa. As can be seen on the map , the country almost entirely fits within the borders of the Ethiopian highlands. After the separation of the former province of Eritrea in 1993, she has no access to the Red Sea. Although the coast (in the Bab el-Mandeb Strait) from the Ethiopian border is only 50 km away.
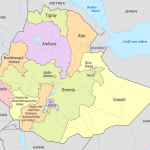
The political map shows that Ethiopia is bordered by six states. In the north, it is the former province of Ethiopia that gained independence in 1993 – Eritrea, in the west – Sudan and South Sudan, in the south – Kenya, in the south and east – Somalia. Ethiopia’s eastern neighbor is also tiny Djibouti.
Relief
Most of the territory of Ethiopia is a high-altitude plain. It makes up about 2/3 of the country. Eastern Ethiopia is lowland. The highest heights of the country are in the north, where two peaks dominate, the height of which exceeds 4000 m. These are Ras Dashen and Talo. The first exceeds the indicated height by 620 m, and the second by 413 m.
Therefore, a significant part of Ethiopia is rocky high-mountain semi-deserts with small oases along waterways and in valleys. The eastern part of the country has even more difficult climatic conditions, fewer rivers and arid lands.
Water resources
Despite the highlands, Ethiopia as a whole does not lack water. The western part of the country is rich in rivers and lakes. The largest river in the country is Abbay , better known in the world as the Blue Nile, which eventually absorbs almost all the waters of the western rivers of Ethiopia and carries them to the great Nile.
There are also many lakes here. The largest of them is Tana. It is flowing and so full of water that it supplies energy to the country through a hydroelectric power station built at the source.
In the east of Ethiopia, there is a shortage of water. There are few rivers here. Even the Jubba , the largest river in Somalia, does not seem large in Ethiopia.
The largest cities on the map of Ethiopia
- Addis Ababa (more than 3 million inhabitants). Almost a quarter of the total population of the country lives in the capital of Ethiopia. The city was founded in the late XIX by the decree of the Ethiopian emperor Menelik II and was immediately built as a capital. According to the Constitution, Addis Ababa is equated to a whole province. The city is distinguished by a variety of economic activities and is the most important transport hub. “New Flower” is the cultural, political and economic center of Ethiopia.
- Dire-Dawa (400 thousand). The impetus for the development of the city, as well as the capital, which has a special status, was the construction of the Ethiopian-Djibouti road, which connected the capital with a major seaport in neighboring Djibouti. The disengagement of Eritrea further increased the importance of Dire Dawa, located in the northeast near the Djibouti border , since now Ethiopia does not have its own coast and is able to conduct maritime trade only through Djibouti.
- Adama (Nazret) (300 thousand). This city with a biblical name (Nazareth), officially called Adama, also grew due to the fact that it is located on the highway and railway leading to Djibouti. The whole life of Adama, located just 100 km from Addis Ababa, revolves around these roads.
- Gondar (260 thousand). The city is located in the north of the country, near Lake Tana, in the most fertile region, which made it the center of Ethiopia’s largest agricultural region. There are many enterprises of the food and processing industries. In addition, Gondar is the historical capital of the country. It was here that the residence of the Ethiopian emperors was located for a long time.
 The Guide Maps
The Guide Maps