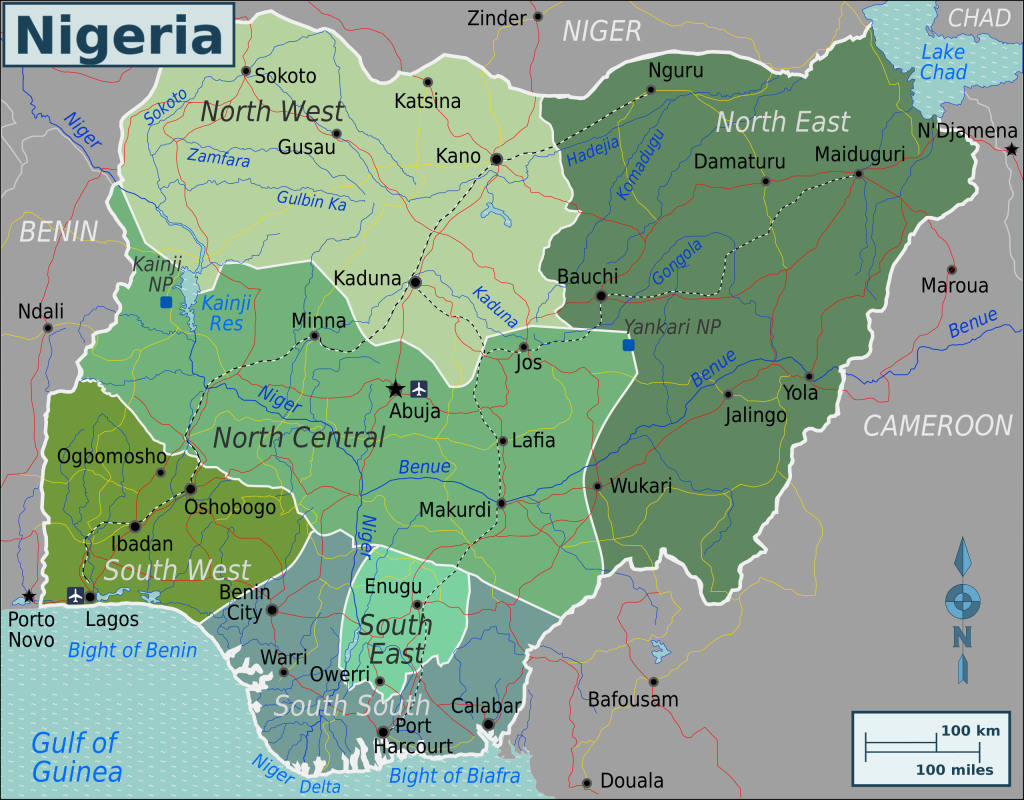
Map of Federal Republic of Nigeria
Nigeria map online
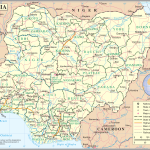
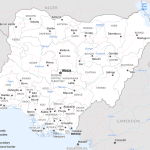
- Nigeria political map
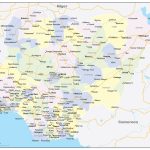
- Administrative divisions of Nigeria with signed cities
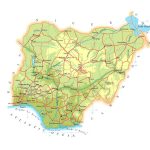
- Detailed physical map of nigeria
General description of the Federal Republic of Nigeria
The Federal Republic of Nigeria is a state located in the south of the Western region of the African continent. The name of the country was formed from the name of a large water body of the same name – the Niger River, which occupies the third place in length on the mainland.
Historically, the state of Nigeria was formed in the 18th century as one of the African colonies of Great Britain. From the beginning of the 20th century until obtaining the status of an independent state in 1960, it was referred to as British Nigeria. Previously, separate settlements and states of African peoples were located on the territory of modern Nigeria.
With a relatively small territory occupied by the Republic of Nigeria on the mainland – 923.8 thousand km², it is in first place in terms of population in Africa and in seventh place in the world ranking – 216.8 million people. The population of the country speaks the state English, as well as the languages of the indigenous peoples of the Igbo, Yoruba, Hausa, Fula and others. In Nigeria, as in most African states, there is a large number of indigenous peoples whose history began long before their colonization, which is confirmed by archaeological excavations.
The modern capital of the republic – the city of Abuja with a population of about 1.5 million people, has been functioning as the capital since 1991.
Location of Nigeria on the world map
Geographically, Nigeria on the world map is located on the African mainland, on the coast of the Gulf of Guinea of the Atlantic Ocean, which washes it from the south. From the west, north and east, the state borders on Benin, Niger, Chad and Cameroon, respectively. The close location of the Earth’s equator provides a hot climate and high humidity throughout its territory. The largest amount of precipitation is recorded in the Niger Delta (up to 4 thousand mm per year), in other parts of the country, precipitation is much less – from 0.5 to 1.5 thousand mm per year. The high humidity of the climate is maintained by the warm GW hoar current, which originates at Cape Almadi and runs along the entire coast of West Africa to the Namib Desert .
Relief
The Niger River conditionally divides the territory of Nigeria into two parts: a flat part in the south and a plateau in the north. The plains of Nigeria, covered with tropical forests, occupy almost all river valleys. Gradually, tropical forests turn into humid African savannahs, and in the north of the country into dry tropical forests. However, with the development of cities and agriculture, the forest area in Nigeria is declining.
The northern part of the area is characterized by a gradual transition to a plateau with small hills in the form of rocks: the Jos plateau , Yoruba and others, the climate of which is more arid.
Hydro resources
Niger is the third longest (4,180 km) and basin volume (2,117.7 thousand km²) river in Africa. Starting on the slope of the Leono -Liberian Upland, it flows through almost all states located in southern West Africa and flows into the Gulf of Guinea.
The Niger and its tributaries are of great importance for the development of the region. It is thanks to the large supply of fresh water in the territory of Nigeria that a state formation has historically developed. The largest left tributary of the Niger on the territory of the republic is the river Benue , 1400 km long.
In addition, in the north of Nigeria and the border states is the ancient Lake Chad, the water level in which depends on the water level in the rivers flowing into it. The shores of the lake are heavily swamped, and the dry climate increases their area.
Flora and fauna
Large water bodies of the country have contributed to the natural diversity of flora and fauna. In the river valleys in the equatorial forests, a large number of trees grow that do not shed their leaves for more than two years and do so at different times, due to which the forest is constantly green. Trees reach 40 meters and from a bird’s eye view are “green rivers”. Various palms, ficuses, sandalwood, nutmeg and redwoods, as well as ferns, lianas and orchids are common in Nigeria.
In the savannahs of the central and northern regions of the country, a large number of tall herbaceous plants and free- standing trees such as baobabs, cayas , isoberlines grow .
The fauna in the republic can be seen in national parks. In the natural environment live giraffes, rhinos, elephants, leopards and a large number of antelopes. In the forests there are various types of monkeys, including gorillas, and various representatives of the bird family: toucans, hummingbirds, turacos .
Major cities on the map of the Republic of Nigeria
Given the high population density compared to other African countries, Nigeria has more than 10 cities with a population of over a million people. The largest of them:
- Lagos is the largest city of the republic, which until 1991 was its capital. One of the oldest cities on the African continent. The main city of the Yoruba people, founded by them in the 13th century, was later the capital of British Nigeria. The current population of the city is about 13 million people, and with the settlements adjacent to the city – 21 million people, which is the highest figure in Africa. Due to its location on the coast of the Gulf of Guinea, the city is a seaport and economic center of the country.
- Ibadan is a large industrial city in Nigeria with more than 5 million people. The city began to exist in the middle of the XIX century and is located on the border of tropical forests and savannahs. The food, textile, tobacco industries and agriculture are developed here. The population is also employed in the banking, insurance, and scientific fields.
- Kano– the third largest city in the country (3.8 million people). Built by the Hausa people in the drier northern part of Nigeria. Historically, it was a major trading center of the kingdom, but during the British protectorate and after it became part of the republic.
- Benin City is the oldest city of the republic, located 330 km east of Lagos with a population of just over 2 million people. The city is the academic capital of Nigeria: here are the best universities in the country. Historically, art crafts developed in the city and its environs, especially woodcarving and ivory, the creations of which were exported in large quantities by the colonialists. The city has preserved historical sights that arose during the period of the Kingdom of Benin ( XIV – XVII centuries).
- Port Harcourt is a city built in the Niger Delta in 1912 by the British colonizers. The current population of the city is just under 2 million people. The city is the capital of Rivers State , and, due to the relatively new construction, the city has a convenient infrastructure: an international airport, seaports, stadiums, universities.
- Kaduna is one of the northern cities of Nigeria with a population of about 2 million people. The city was founded at the beginning of the 20th century and is now a major industrial center for mechanical engineering, petrochemical, and textile industries. Kaduna is the birthplace of famous Nigerian football players Daniel Amokachi , CelestineBabayaro and others.
Major tourist destinations in Nigeria
Favorite tourist destinations that attract tourists to the country are the national parks of Nigeria, which are located almost throughout the country: Chad Basin , Cross River, Gashaka Gumti , Yankari and others. Here you can see the protected flora of tropical forests and savannahs, meet animals and birds living in the wild, see picturesque waterfalls and rock formations.
- In Southwestern Nigeria , located on the coast of the Gulf of Guinea, which includes the states of Lagos, Ekiti , Ogun , Ondo , Osun , Oyo , tourists can visit the largest city on the African mainland – Lagos. Here you can see tropical forests and their inhabitants.
- In the South-South of Nigeria (the states of Rivers , Edo , Delta, Bayelsa , etc. ), cities with European architecture built in the British period are popular.
- Southeast Nigeria (states of Abia , Ebony , Enugu , Imo , Anambra ) is mainly an industrial region where natural resources are mined and industrial production is located.
- North Central Nigeria , in addition to the states of Benue , Kogi , Kwara , etc., also includes the capital territory of Abuja. Here you can see the modern architecture of the country combined with African nature.
- The composition of Northwestern Nigeria includes the states of Jigawa , Kaduna , Kano , Katsina and others. Here tourists will be interested in visiting the sights of the ancient city of Kano or the mountain landscapes of Kagoro .
- Northeastern Nigeria (the states of Bauchi , Borno , Gombe , Yobe , etc.) is known for its national parks with rocky hills, here you can visit the relict Lake Chad, the area of which is getting smaller every year.
 The Guide Maps
The Guide Maps