Map of Islamic Republic of Pakistan
Pakistan map online
- Political map of Pakistan with borders of neighboring states
- Physical map of Pakistan with relief and bodies of water
- Pakistan tourist map
- Large detailed map of Pakistan with cities and towns
General description of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan
The Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a young country that appeared on the world map only in 1947 as a result of the partition of a part of India that had been under British rule for a long time.
Islamabad has been the capital of the country since 1967.
The literal translation of the country’s name in Persian means “land of the pure “. It was invented back in 1933 by an active figure who advocated the independence of the state, Rahmat Ali.
Pakistan occupies a significant territory on the world map, being the second largest country in South Asia. The state is located at 881,913 kilometers and has a coastline of 1046 kilometers.
Pakistan is the fifth most populous country in the world with 218,066,558 people. Of these, 205 million are Muslims.
The Federal Republic consists of four districts and tribal parts of the country.
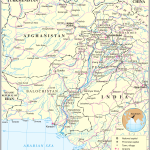
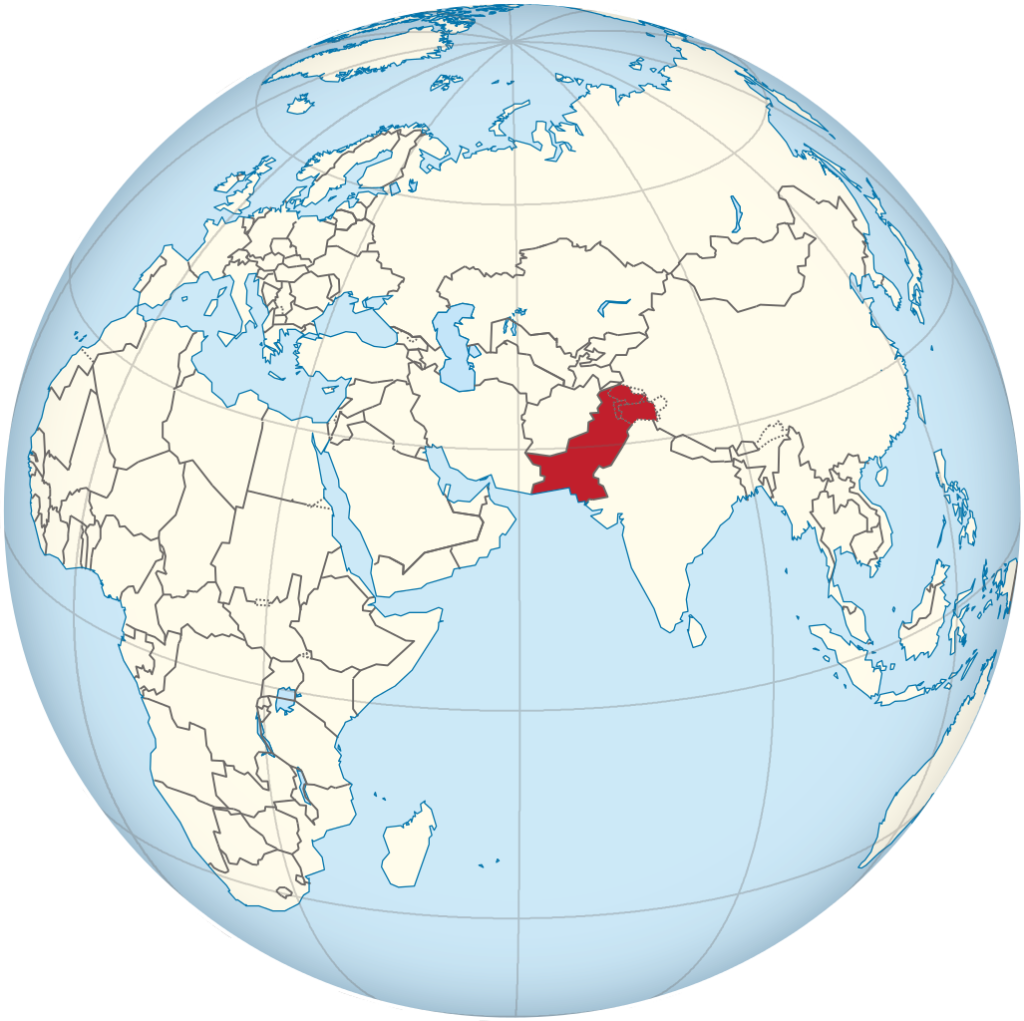
Location of Pakistan on the world map
The state, located at the crossroads of Central, South, Western and East Asia, stretches for 1,500 kilometers.
The east of Pakistan is represented by a low-lying plain, the north is characterized by hilly terrain and the presence of rocky places.
From the east, the state borders with India, in the west with Afghanistan, the Wakhan corridor of which separates the country from Tajikistan, in the southwest with Iran and in the northeast with China. The country is located on the coast of the Arabian Sea and has a maritime border with Oman.
The plain is represented by a dry continental climate. The northwest has subtropical weather conditions. In the mountains of the northern part of the country, more precipitation falls, so the air is more humid there.
Climate
In winter, it is warm in the east of the country, the air temperature does not fall below +12°C, and on the coast it stays around +20°C. High-mountainous areas are characterized by cold winters and temperatures down to -20 °C.
Summer in Pakistan is hot. In deserts, the temperature rises above 35°C, in coastal areas around 29°C, in mountains and plateaus 20-25°C. On the tops of the mountains, the temperature never exceeds 0 °C.
In the deserts, only 50 mm of precipitation falls per year, on the plain – 400 mm, in the foothills up to 500 mm and about 1500 mm in the mountains.
Frequent winds bring warm dusty masses from the desert and cold from the mountains. The contrast of natural and climatic conditions leads to different weather in areas of the same territory. The weather in the regions of the country differs even more.
The relief of the country
Looking at the geomorphological map of Pakistan, one can clearly distinguish two large orographic regions – the Indian Plain and the mountains and uplands surrounding it.
The plain in Pakistan has a flat landscape with slight slopes and is located 200 meters below sea level. It is one of the largest alluvial plains and runs from the foot of the Himalayas to the Arabian Sea. Its length is 1200, and the width is about 550 kilometers.
The Indian Plain is composed of three parts: Punjab, Sindh and the Thar Desert.
The mountain peaks of Pakistan are composed of limestone, sand and schist. On the highest mountains there are gorges and rivers, and on the peaks there is snow.
On the territory of the state there are about forty mountain ranges, the height of which exceeds 7000 meters.
The highest elevations are Mount Tirich mir with a height of 7690 meters and Mount Chogori with a height of 8611 meters.
The mountains contain rich deposits of oil, coal, chromite ore, ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
The mountainous part of Pakistan has tectonically active zones. Natural disasters often occur in these places: avalanches come down, mudflows, rockfalls occur. So, in 1935, an earthquake occurred in the city of Quetta , as a result of which thirty to sixty thousand people died.
Water resources of Pakistan
Most of Pakistan’s water resources are the Indus River Basin. The rivers located in the western part of the country drain into the Arabian Sea or are closed. The Sutlej River , being the main tributary of the Indus, collects the waters of the main rivers of the country and gives water to irrigation canals.
Natural World of Pakistan
On the flat terrain in the river areas there is fertile soil, in the interfluves – semi-desert gray soils.
The Thar Desert is dominated by sands, on which dry shrubs and tough vegetation grow.
In some places along the rivers you can see forests of poplar and tamarisk. Artificial irrigation makes it possible to grow rice, cotton, wheat and other crops.
At an altitude of 20 00–2500 meters above sea level, large areas are occupied by tall forests of evergreen trees.
Animals of different species inhabit Pakistan: leopards, hyenas, brown and white-breasted bears, kulans, foxes, wild goats, antelopes, gazelles, rams and crocodiles. There are a lot of poisonous snakes, scorpions, ticks in the country.
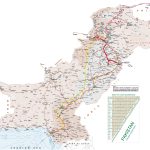
The largest cities on the map of Pakistan
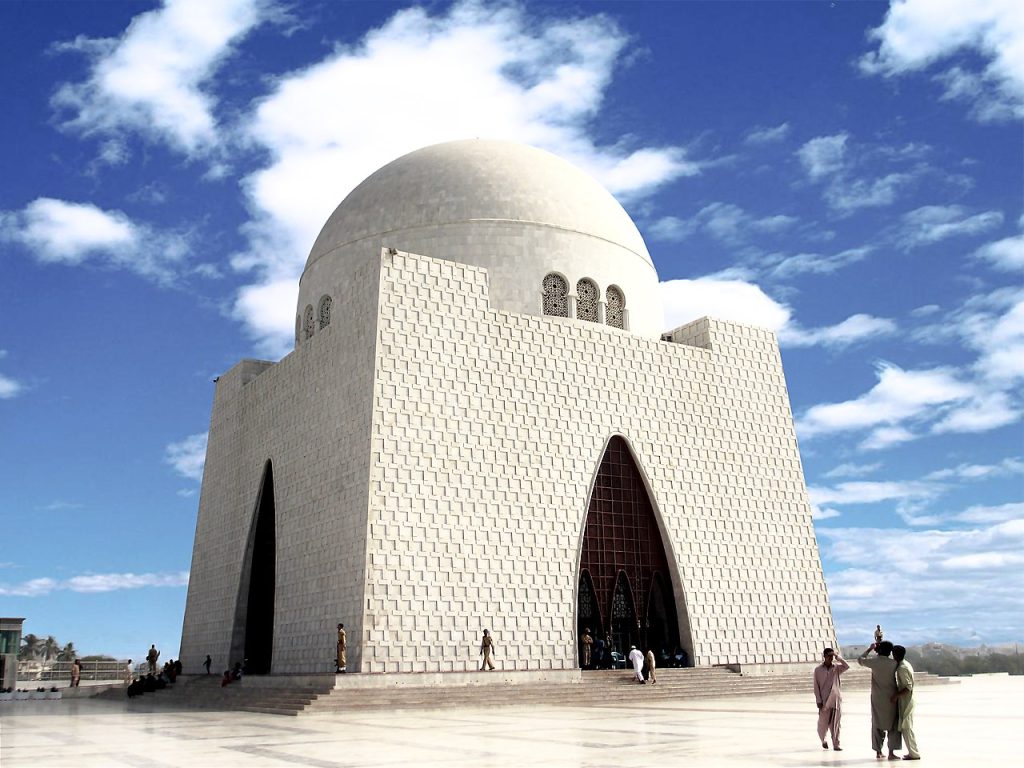
Karachi
Karachi is a large port city and financial center of Pakistan, located in the south of the country.
The area of the settlement has 3527 kilometers.
Karachi has a population of 23,500,000 . This population is due to the resettlement of hundreds of thousands of migrants from the Eastern regions of Pakistan, India and other parts of the southern region of Asia.
It is the main economic, industrial and commercial center of the state. The largest organizations are located in Karachi, textile factories and machine-building plants, scientific and medical institutes are concentrated.
Lahore
Lahore is the capital of the Punjab, located on the left bank of the Ravi River.
The border with India is 22 kilometers from the city.
In 2009, the population of Lahore was 10,000,000.
The city has its own airport, museums, a university and a developed film industry.
In Lahore , the production of textiles, the chemical and food industries, and mechanical engineering are developed.
Faisalabad
The city ranks third among the largest settlements in Pakistan and is the administrative center of the Punjab region.
The city was founded in the 18th century, when tribes engaged in afforestation lived on this land.
The city was originally designed for twenty thousand people, but the fertile land attracted a large number of people from the countryside.
During independence, the population almost doubled, rising from 69,930 to 179,000 in ten years. This was mainly due to the migration of Indian refugees. The Industrial Revolution also led to an increase in population, and in 1961 the number of inhabitants exceeded 400,000.
Today Faisalabad is an industrial and agricultural center with a developed production of textiles, chemicals, food and medical products.
Faisalabad has fertile soils, which makes it one of the leading agricultural areas. Residents of the city are engaged in the cultivation of cotton, wheat, oranges, bananas, apples, tangerines, mangoes and sugar cane.
There is also a large rice factory in Pakistan.
Rawalpindi
Rawalpindi is a city located near Islamabad.
It ranks fourth in the list of the largest cities in Pakistan.
In 1959, the settlement was designated as the temporary capital of the state.
Rawalpindi is home to about 2,000,000 people.
The main center of Sikh pilgrimage is Gurudwara .Panja Sahib is located 30 km from the city.
Multan
The city is located in the Punjab region.
The settlement is located 124 meters above sea level.
The main part of the inhabitants profess Islam.
The city has railway lines and an international airport.
Fertilizers, cosmetics, textiles and agricultural raw materials are processed in Multan .
In addition, handicraft production of ceramic dishes and carpets flourishes in the city.
Gujranwala
A city and administrative center located in the Punjab region.
The settlement is located on the Great Wheel Road, which connects the city with other administrative centers.
The city is located at an altitude of 249 meters above the sea.
Textiles, ceramic and metal utensils, leather goods, safes are made in Gujranwala .
The city grows sugar cane, melons and grain for export.
Hyderabad
Hyderabad is a city in the province of Sindh , founded on the site of a fishing village in 1768.
The settlement is located 12 meters above sea level.
Hyderabad has a very rich cultural history. Traces of the Indus civilization have been found here.
The city has many architectural monuments. True, most of them were damaged or destroyed during the struggle for independence.
Hyderabad was a haven for Sindhi poets, and therefore is considered the literary home of the local Sindhi language.
Nowadays, Hyderabad is known for its educational institutions and widespread child labor.
Tourist regions of the country
Pakistan began to attract tourists in the 1960s thanks to the hippie trail. However, political events taking place inside the country led to the fact that in the 1970s it was included in the list of countries unsafe to visit.
Despite this, tourists continue to be attracted by the unique landscapes and unusual culture of Pakistan.
Architecture lovers are attracted by the monuments of the Mughal era. Those who enjoy history can wander through the ruins of ancient civilizations such as Mohenjo-Daro , Harappa, and Taxila . Extreme travelers go to Pakistan to go mountain climbing.
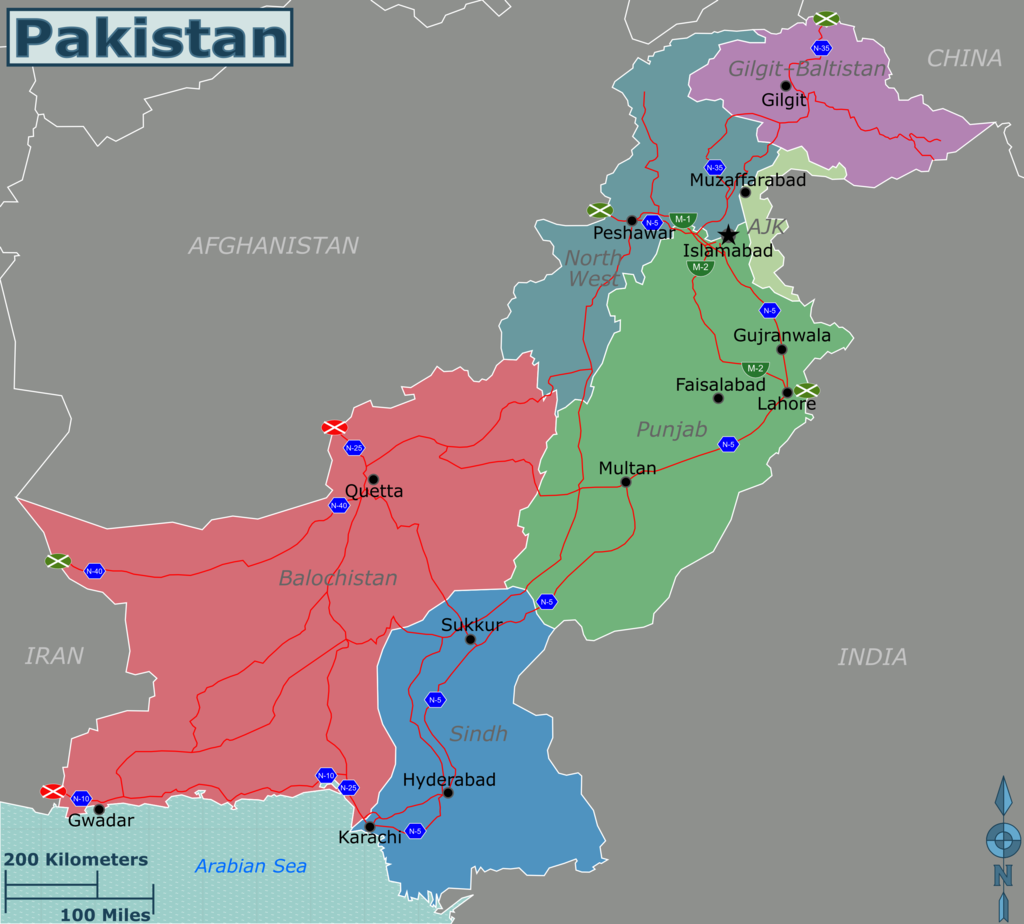
The country is made up of four provinces: Punjab, Sindh , Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Balochistan.
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa is abbreviated as PC or KPC.
It is the third city of Pakistan in terms of territory, its area is 74521 kilometers. The region is home to 35.5 million people.
The province includes nine administrative centers.
The city borders the rest of Pakistan to the south and east, central Afghanistan to the west, and the Wakhan Corridor to the north.
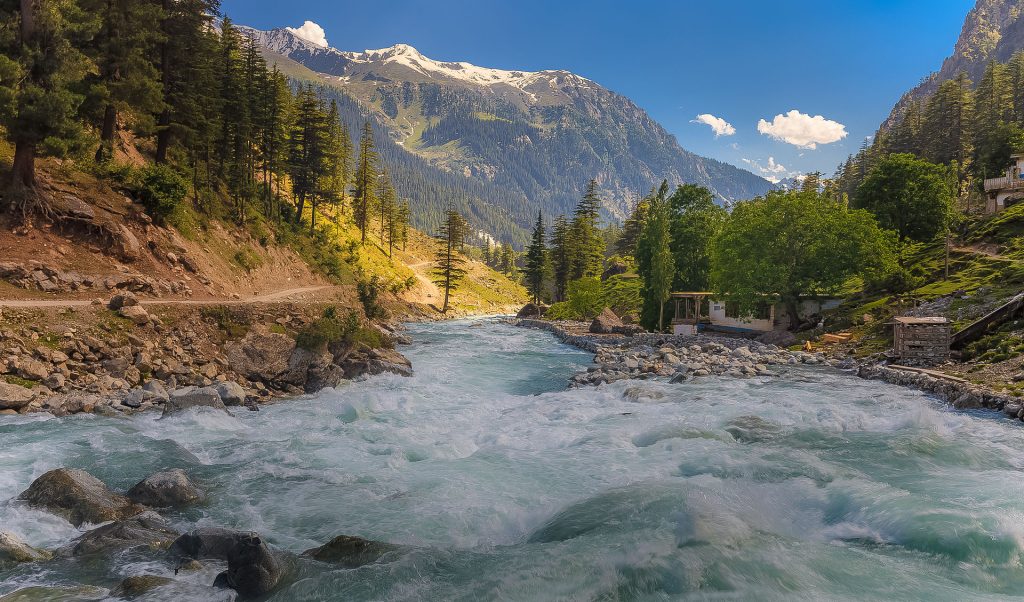
The terrain of the KPK is mountainous and is considered one of the most beautiful in the country.
There are many tourist attractions in the province:
- Swat Valley is one of the most picturesque places where the Swat and Ushu rivers flow, waterfalls rush down, and snow-capped peaks invite skiing enthusiasts.
- The Kumrat Valley is a valley covered with lush green grass, surrounded by dense forests, snow-capped mountains and misty hills. The fast flowing river Panjkora flows through the valley . The place attracts tourists who appreciate the beauty of nature and prefer to camp in tents.
- Ayubia National Park is an ecologically clean place under the protection of the Department of Wildlife and Parks of the Government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa . Consists of coniferous, broad-leaved and mixed forests. The park is a resort complex from a combination of four mini-resorts. There are 104 plant species, 203 bird species and 31 mammal species in the park.
- The Khyber Pass is a 1,067 meter high break in the rock. The rock is located on the border of Afghanistan and Pakistan.
Punjab
The most fertile region of the country with a large number of inhabitants and many shrines and mosques.
It is a place of pilgrimage for Sikhs from all over the world.
Khewra Salt Mine is located in northern Punjab and attracts thousands of tourists. It ranks second in the world in size and is the main attraction of Punjab. There are many pools of salt water inside the mine. Tourists are delivered to the mine by a special train.
Another attraction in the northern part of the province is the preserved Fort Rohtas , the construction of which dates back to the 16th century.
Sindh
Sindh is the historical homeland of the Sindhi people. The city is home to over 45 million people, making it the second most populous city after Punjab.
It has a distinctive culture and traditions dating back to the civilization of the Indus Valley.
Sindh is the largest center of economy and finance.
It has two regions and seven administrative units.
ancient settlement of Mohenjo-Daro is located in northern Sindh . This archaeological site is under the protection of UNESCO and is considered one of the main historical monuments of southern Asia.
In the southern part of Sindh is Kirtar National Park . This is a place with a unique landscape and pristine natural beauty. The park is home to a large number of birds, mammals and reptiles, hunting of which is prohibited.
Another attraction of Sindh is the freshwater lake Kinjhar , which is used as a source of drinking water for nearby cities. On weekends and holidays, people come to the lake to relax on the shore, swim and fish.
is a small but very ancient city of Sehwan in the province of Sindh . It is the burial place of the great mystical poet, scholar and saint Lal ShahbazKalandar , who lived here in the 13th century. Thousands of believers flock here every year to pay tribute to the memory of the saint.
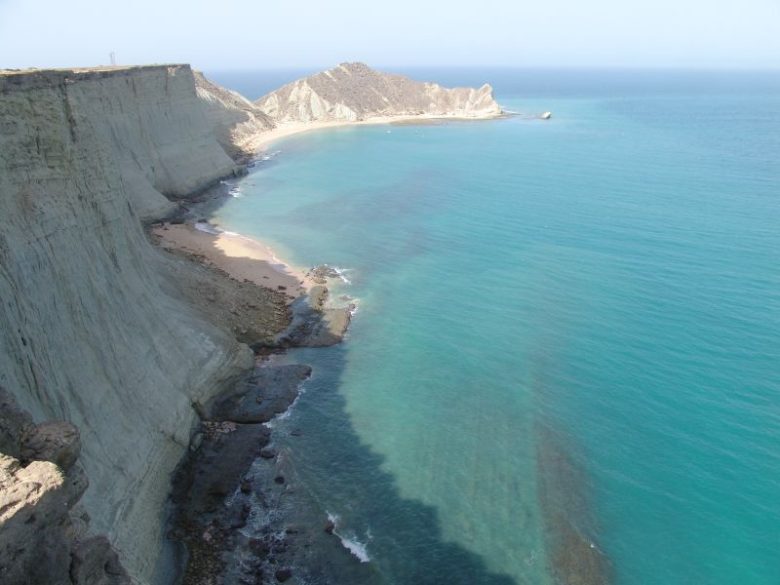
Balochistan
This is one of the most remote, large, but at the same time underdeveloped provinces of Pakistan.
Balochistan suffers from a lack of water resources, a poorly developed economy, poor governance and terrorism.
One of the attractions of Balochistan is Khanna Lake with turquoise water. There are goldfish in the lake, which fearlessly swim to the shore, causing delight among tourists. Tall pines are planted around the lake.
Hazarganji-Chiltan National Park is another favorite place for tourists. According to legend, countless treasures are buried in the mountains of this park. The park is home to many animals that can be seen when visiting. Near the entrance to the park there is a small museum of natural history.
The largest park in Pakistan, the Hingol National Park, is also located here . It covers an area of 1650 kilometers.
In Balochistan there are Archaeological and Geological museums. The first contains collections of ancient weapons, manuscripts, and coins. In the geological museum you can see rocks and fossils found in this province.
 The Guide Maps
The Guide Maps