Map of Japan
Japan map online
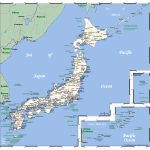
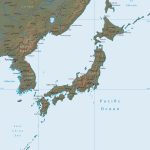
- Detailed map of Japan with city names
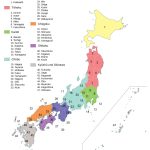
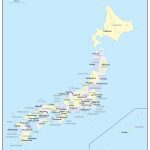
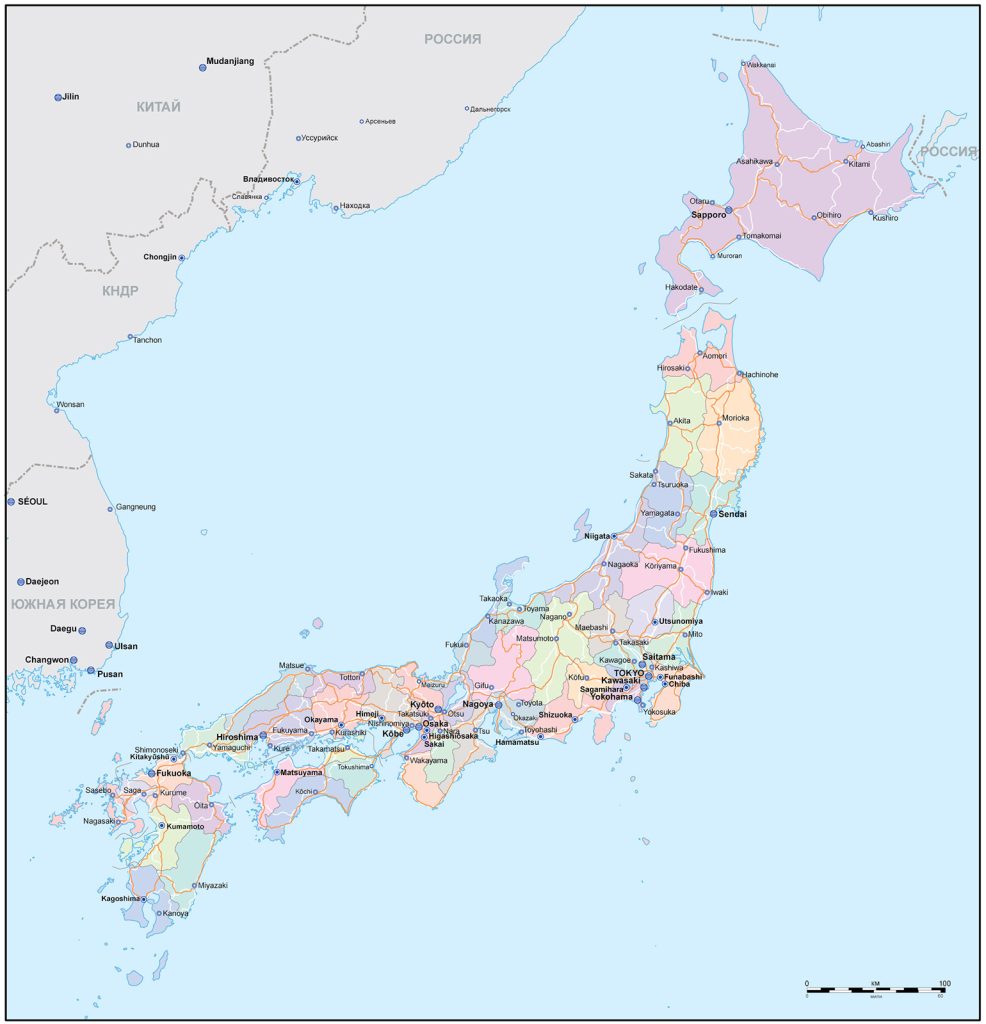
- Administrative divisions of Japan with names
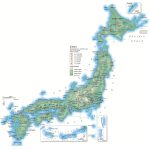
- Relief and population by cities in Japan
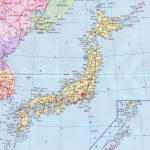
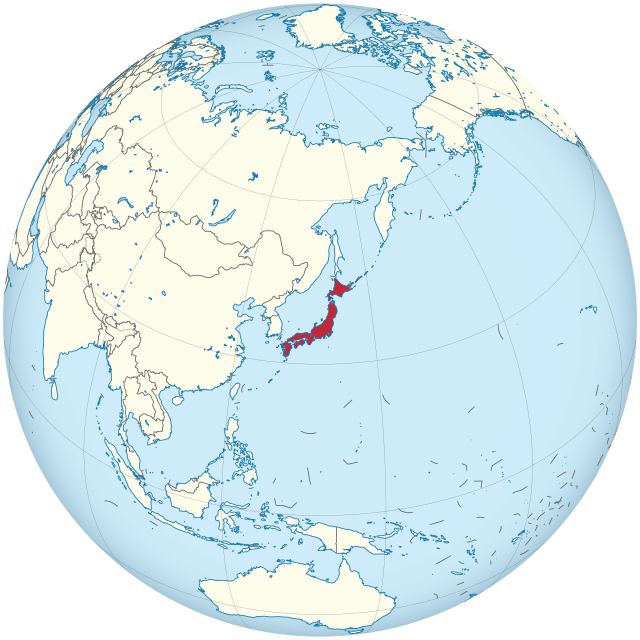
- Location of Japan in East Asia
- Administrative boundaries of the districts of Japan
General description of the Japan
Japan on the map is located on a large island archipelago off the southeastern edge of the Eurasian continent. However, geographers attribute it to the East Asia region.
The total area of the Japanese Islands is more than six thousand islands – 372.8 thousand square meters. km. This is more than the area of neighboring Korea, but several tens of times smaller than the area of neighboring China. The closest country to Japan in terms of territory is Germany.
Japanese islands of volcanic origin. Therefore, the highest mountains are dormant volcanoes. However, the highest is Fujiyama (3776 m) on the island of Honshu. The remaining peaks are inferior to it by more than 1000 m.
The map of Japan is very long from north to south, and therefore resides in several climatic zones at once. Cold, almost Siberian winters happen on the island of Hokkaido. Most of the island of Honshu has a typical insular temperate climate with a clear division into four seasons. The southeastern (Pacific) coasts of the Japanese Islands experience hot summers and sometimes cold, snowless winters. But the island of Kyushu and all of southwestern Japan are located in the subtropical climate zone.
The capital of Japan – the largest (more than 14 million people) city of Tokyo – is located on the southeast (Pacific) coast of the island of Honshu. Its location is close to the geometric center of Japan.
Also the largest and most significant cities of the country are:
- Yokohama (3.71 million inhabitants)
- Osaka (2.69 million)
- Nagoya (2.28 million)
- Sapporo (1.93 million)
- Kobe (1.54 million)
- Fukuoka (1.52 million)
- Kawasaki (1.5 million)
- Kyoto (1.46 million)
- Saitama (1.25 million)
Location of Japan on the world map
Japan is an island nation with 6,852 islands. It is entirely located on the islands of the large Japanese archipelago (the largest islands are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu), which is located at the eastern edge of the Eurasian continent. The Japanese islands stretch in a semicircle from the southern tip of the Korean peninsula to the southern shores of Sakhalin Island and the Kuril Islands.
Japan, for the above reason, does not have land borders. However, the map shows that the country’s maritime neighbors are the following states: in the north – Russia, in the south – Taiwan, in the west – China, South Korea and North Korea. To all except Taiwan, Japan has territorial claims.
Relief
75 percent of Japan’s territory is hilly and mountainous, which is explained by the volcanic origin of the islands. The lowest parts of the country are the coasts. Low-lying areas in the interior of the islands are not found. On the maps of all the islands, mountain ranges are clearly visible, which are almost everywhere and occupy the central part of the land. The only exception is the islands of the Ryukyu archipelago : they are flat with hills.
The highest mountain in Japan and the islands of Honshu is Fuji (3776 m), the islands of Hokkaido – Asahi (2290 m), the islands of Shikoku – Ishizuchi (1981 m), the islands of Kyushu – Kuju (1788 m).
Water resources
The mountainous relief did not allow the formation of the river system. Japanese rivers, as a rule, are small, short, but full-flowing fast mountain rivers. They flow into the ocean from the peaks, not having a large number of tributaries. The rivers are practically not used for navigation due to the difficulties of navigation, but hydroelectric power plants have been built on most of them. The largest rivers of the country are Kitakami, Shinano, Ishikari, Tone , which are “lucky” to flow in low-lying places.
There are few lakes in Japan. All of them are located in the craters of extinct volcanoes and in tectonic faults. The largest Lake Biwa (670 sq km) is located near the city of Kyoto.
The largest cities on the map of Japan
- Tokyo (about 14 million inhabitants). The capital of Japan is so large that it is administratively, economically, territorially and culturally divided into special areas, which have separate prefectures. There are 23 of them: Adachi, Edogawa, Arakawa, Chuo, Bunkyo, Toshima, Itabashi, Chiyoda, Katsushika, Taito, Kita, Setagaya, Koto, Sumida, Minato, Suginami, Meguro, Shinjuku, Nakano, Shinagawa, Narima, Shibuya, Ota. The Tokyo metropolitan area is one of the largest in the world. According to experts, Tokyo is the most economically successful city in the world. It has the largest annual turnover among all metropolitan areas in the world.
- Yokohama (3.71 million). Neighbor city of Tokyo. Located just 30 km west of it, on the other side of Tokyo Bay. A large shopping center, a center for shipbuilding, biotechnology and the semiconductor industry. Yokohama bears the unspoken title of the “Gate of the World”, since for a long time foreign ships could moor only in the local port.
- Osaka (2.69 million). Located to the west of Tokyo and Yokohama, in the central part of the island of Honshu. It has an atypical landscape for Japanese cities – it is exceptionally flat. Since ancient times, it has been considered the trading capital of Japan and continues to fight for this status. And yet today Osaka is more of a banking and industrial center.
- Nagoya (2.28 million). It is also located on the island of Honshu, in the valley of several hundred rivers, rivulets and streams. A large commercial and industrial center, which is famous for its metallurgical, chemical, textile, oil refineries. A significant part of Japanese clothing and footwear is made in Nagoya.
 The Guide Maps
The Guide Maps