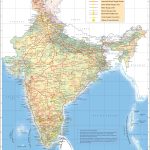
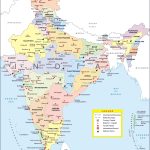
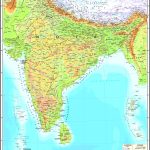
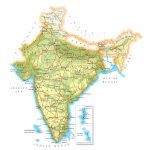
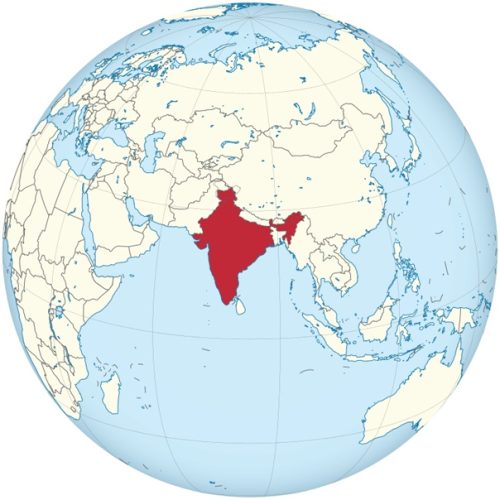
Map of India
Republic of India map online
- Large detailed administrative map of India with major cities
- Large physical map of India with relief and bodies of water
- Large elevation map of India with roads, cities and airports
- Large detailed political and administrative map of India with relief, roads, railroads and major cities
General description of the Republic of India
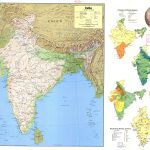
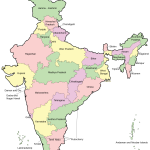
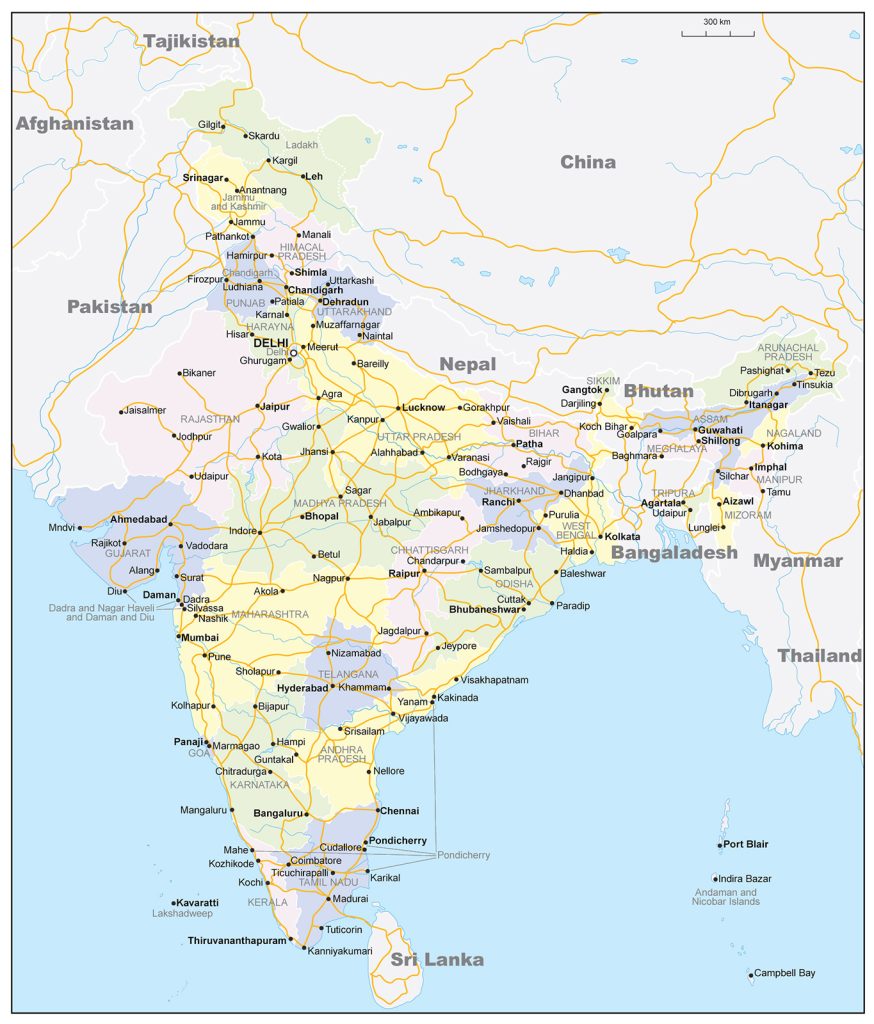 The Republic of India is the largest country in South Asia. The name comes from the Persian Hindu word for the Indus River, which flows through Indian territory. Its area is about 3.3 million km2 ( the seventh largest in the world). In terms of population – over 1.4 billion people, India is slightly inferior only to China. The capital of the country is the New Delhi district of the city of Delhi. India on the map is divided into 28 states and eight union territories.
The Republic of India is the largest country in South Asia. The name comes from the Persian Hindu word for the Indus River, which flows through Indian territory. Its area is about 3.3 million km2 ( the seventh largest in the world). In terms of population – over 1.4 billion people, India is slightly inferior only to China. The capital of the country is the New Delhi district of the city of Delhi. India on the map is divided into 28 states and eight union territories.
In the Indian subcontinent, the ancient Indus civilization arose. Important trade routes passed through India for a long time. The country was distinguished by wealth and culture. India is the birthplace of a number of religions – Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Jainism.
In modern times, the development of the country was held back by its colonial status. Since achieving independence in 1947, India has made significant economic and military progress. However, these successes have not yet been reflected in the standard of living of a significant part of the population that remains poor.
Location of India on the world map
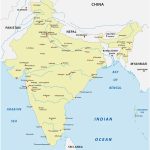
As can be seen on the map , India occupies the predominant part of the Indian subcontinent. The country borders:
- with Pakistan in the west;
- with China, Nepal and Bhutan in the northeast;
- with Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east.
The disputed (with China) territory of Ladakh borders Afghanistan. There are also water borders with the Maldives, Indonesia and Sri Lanka.
India includes the Lakshadweep archipelagos in the Arabian Sea and the Andaman Islands in the Bay of Bengal.
Relief
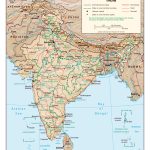
Himalayas – the natural border with China, cross the entire territory of the country. The highest (8586 m) Himalayan peak of India – Mount Kanchenjunga, rises in the state of Sikkim . In the north of India, in the disputed (with Pakistan) region of Kashmir, there is a high-altitude Karakorum mountain range, and in the northeast – moderately high Asamo – Burman mountains and the Shillong mountain plateau .
In the depths of the Hindustan peninsula, the Deccan plateau stretches, the faults of which formed medium-high mountains and plateaus. In the western and eastern directions, the relief of the plateau rises, forming the mountain ranges of the Ghats with steep slopes. The Thar Desert is located in the northwest of the country.
Water resources: seas, rivers and lakes
The southern part of India is washed by the Indian Ocean and its water regions – the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. The country’s coastline stretches for more than 7.5 thousand km. About 5.5 thousand km of them are in peninsular India, and the rest – on the islands.
After the partition of British India, the predominant part of the Indus River went to Pakistan. The main rivers of India proper are the Ganges and the Brahmaputra. Both have Himalayan sources and flow into the Bay of Bengal. Other notable rivers also reaching this bay are Godavari, Kaveri , Mahanadi, Krishna and Kaveri . And the rivers Narmada and Tapti flow to the Arabian Sea. There are few lakes in India, and they are all small.
Climate
The climate of the country is largely determined by the influence of the Himalayan mountains and the Thar desert. The Himalayas block the path of cold winds, softening the climate. The Thar Desert, on the contrary, attracts summer monsoon winds, which contribute to rains in the summer-autumn period. On the territory of the country, four groups can be distinguished with prevailing types of climate – two tropical – wet and dry, humid subtropical, mountainous.
Three weather periods are distinguished in the main territory of the country :
- hot and humid June – October;
- cool and dry November – February;
- very hot and dry March-May.
The wet season accounts for 80% of the annual precipitation. The town of Cherrapunji on the slopes of the Shillong Plateau is known as the rainiest place on the planet (about 12 thousand mm). The driest areas are the west of the Indo-Gangetic Plain in the Thar Desert (less than 100 mm) and the center of Hindustan. For May, temperatures of 30–35 0 C are common : sometimes they exceed 45 0 C.
Vegetable world
A third of all plants growing in India are endemic. More than 18 thousand species of flowers grow in the country. Plants characteristic of India are Indian lilac (azadirahta indica) and fig tree (fig tree). Various types of palms are spread throughout the territory – date, coconut, banana, and many types of bamboo.
Forests occupy about 22% of the territory of India. Most of them are deciduous. Coniferous pines, junipers and Himalayan cedars grow in the northern highlands. In the hilly regions of India, pines, firs, spruces and cypresses are widespread.
The largest cities on the map of India
Mumbai
The administrative center of the state of Maharashtra is located in the west of India, on the coast of the Arabian Sea. Mumbai, excluding suburbs, is located at the mouth of the Ulhas River, on the islands of Bombay (the name of the city until 1995) and, in part, Salsette. More than a thousand kilometers separate it from the capital of the country.
Mumbai is the largest port and business center of the west of India. Well-maintained central quarters, where wealthy people live, contrast sharply with the northern slums – a haven for the poor.
Delhi
Delhi is located in northern India on the western bank of the Jumna River, a tributary of the Ganges. The plain in their interfluve is the ancient granary of the country. In the southern part of the city, fragments of ancient mountain ranges have been preserved. The main attractions are the Akshardham temple complex and the Red Fort.
The city has the status of an autonomous union territory. On the map of India , it borders the states of Uttar Pradesh in the east and Haryana on the other sides. The New Delhi area of the city is the capital of India.
Bangalore
This city is the capital of the southwestern state of Karnataka. Bangalore is located on the Deccan Plateau, at an altitude of over 900 meters above sea level. This arrangement significantly softens the summer heat. The distance from Delhi is more than two thousand kilometers.
The main attraction is the Bangalore Palace. Many leading IT companies are concentrated in the city, which is why Bangalore is called the “Indian Silicon Valley”.
Hyderabad
Hyderabad is a city on a plateau in South India, the administrative center of the state of Telangana. It was built next to the Musi River, which still flows through the city from west to east. The distance from the capital is more than one and a half thousand km.
18th century Mecca-Masjid and the 16th century Charminar. with four minarets and arches. The city is one of the centers of the Indian film industry.
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad is the administrative center of the district of the same name in the state of Gujarat in western India. It is located on the banks of the Sabarmati River, which often dries up in summer. Most of the city is built up randomly. The distance from Delhi is about a thousand km.
A tourist attraction is the Mosque of Sidi Bashir (“ Trembling Minarets”). In the vicinity – a modest museum of Mahatma Gandhi on the site of his former ashram.
Chennai
The administrative center of the state of Tamil Nadu (with a predominantly Tamil population) is located in southern India. Until 1996, Chennai was called Madras. The distance from the capital is more than two thousand km. Chennai is one of the main ports of the country.
Different areas of the overpopulated city differ significantly. Historical monuments and cultural institutions coexist with numerous slums.
Calcutta
Kolkata (this has been the official name since 2001) is a city in eastern India, the capital of the state of West Bengal. It was built in the Ganges delta in a swampy area. The distance from Delhi is more than one and a half thousand kilometers.
Kolkata is a major economic and financial center of northeastern India. The city is called the cultural capital of the country.
Main directions of tourism
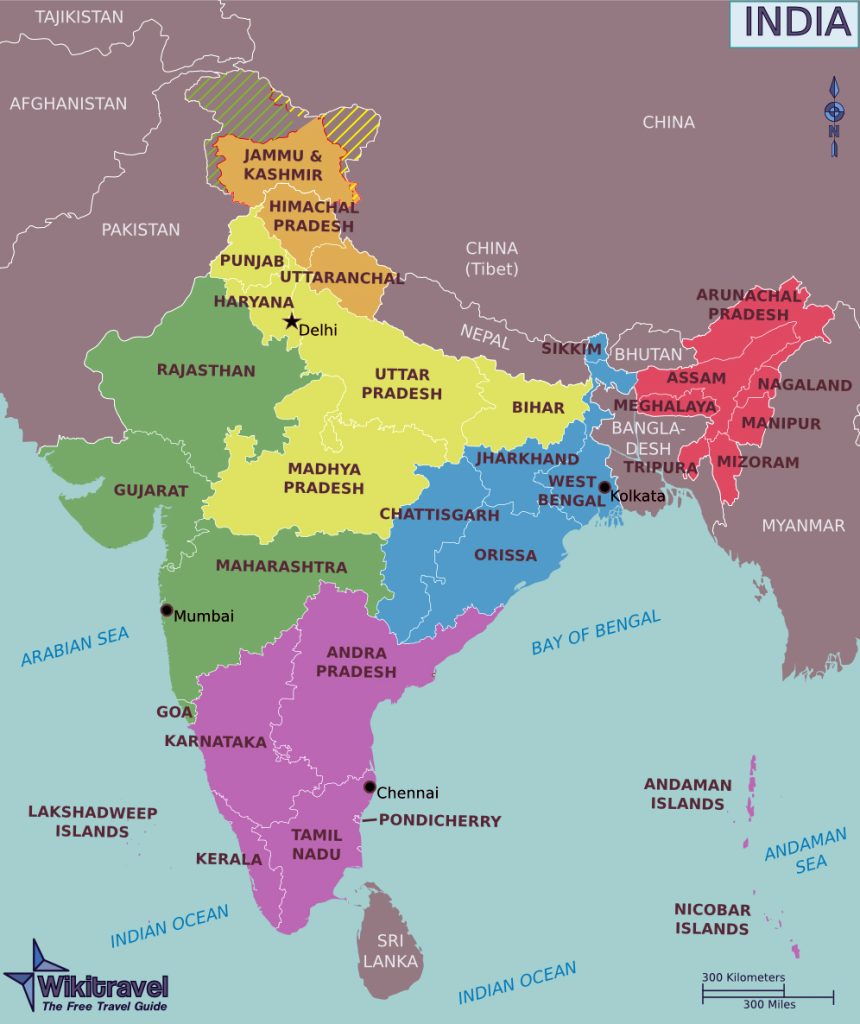 The states and union territories of India are usually divided into several main tourist regions.
The states and union territories of India are usually divided into several main tourist regions.
North Himalayas
It includes :
- the disputed (with Pakistan) mountainous union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, which includes Ladakhk and the Kashmir Valley;
- the northern state of Himachal Pradesh, on whose territory the spiritual center of Tibetan Buddhism is located – the city of Dharamshala with the residence of the Dalai Lama;
- the northern state of Uttarakhand with a very picturesque eastern part.
Plains
On the plains are the states of Bihar, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh and the cities of Chandigarh, Agra and Delhi.
Agra is home to the main attraction of India – the famous Taj Mahal. The Punjab state is the only state in India where the majority of the population is adherents of the Sikh religion. Her main shrine is the Golden Temple, located in the city of Amritsar .
Western India
The region consists of the states of Goa, Maharashtra , Rajasthan and Gujarat , as well as the union territory of Dadra – Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. In Western India, the largest city of the country, Mumbai, is located, the Thar Desert. The state of Rajasthan is known for its architectural monuments, Maharashtra for its rocky caves, and Goa for its forests and beaches.
South India
South India includes the continental states of Karnataka , Kerala , Andha Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Telangana . The island union territories are conditionally included in the region: Lakshadweep is located far to the west, and Andaman and Nicobar are to the east. The greatest tourist attraction is the city of Mysore in the state of Karnataka with a preserved palace, which is considered the second landmark of India (after the Taj Mahal).
Eastern India
The East India region consists of the states of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Sikkim, Odisha and West Bengal. The capital of the latter state is Calcutta, one of the largest cities in India. The region stretches from the mountains to the coast and is characterized by climatic diversity. The temple cities of Bhubaneswar and Konark are located in the state of Odisha .
North East India
This region includes seven states – Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Tripura, Manipur, Assam, called “seven sisters”. The state of Meghalaya is known for its scenic beauty. The region stands out for its religious diversity. The first three states are predominantly Christian. There are large Muslim communities in Nagaland as well as in Assam.
 The Guide Maps
The Guide Maps